
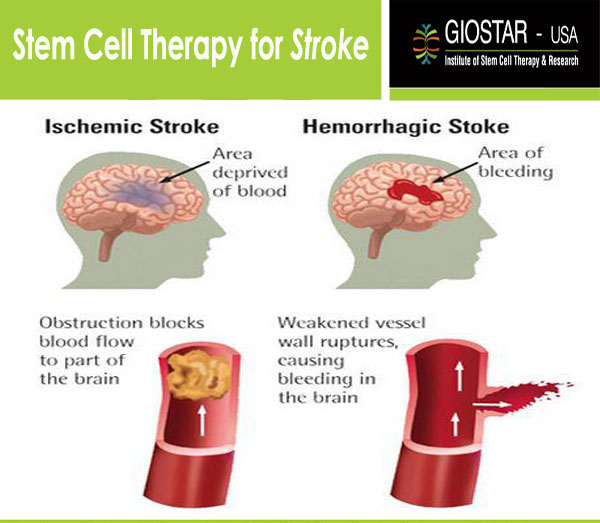

They communicate using chemicals called neurotransmitters, which are essential for neurological function. Neurons are specialized cells that communicate with each other to control all bodily functions. Stem cell transplantation for stroke aims to repair the damage done by the stroke by replacing neurons that have been lost. How Does Stem Cell Therapy Work for Stroke? This process is called transformation and reprogramming. In stem cell therapy, mesenchymal stem cells (these cells can renew and repair themselves) are systematically transferred during the treatment of the affected area and depending on how much damage has occurred. Once administered, they can transform into new neurons and repair damaged tissue. While stem cells can be extracted from several parts of the body like bone marrow, blood, or umbilical cord (which parents nowadays are preserving for in-future use), they can also be created artificially. This includes cells that are found in the brain - neurons. They are unspecialized cells that can transform into a variety of specialized cells. Stem cells are the biological building blocks of all living tissue they are also called regenerative cells that help the different damaged cells to regenerate into new and recovered cells. Strokes occur due to disturbance in the flow of blood due to either blockage in the artery or leaking or bursting of a blood vessel in the brain, which causes brain strokes. If you or someone you love has recently experienced a stroke, this article will answer some common questions about stem cell treatments for stroke treatment. Stem cell therapy remains an experimental treatment for stroke, but its potential is significant. In fact, of the over 800,000 people in the world who experience a stroke every year, about half are left with long-term effects.įortunately, recent advances in stem cell research may soon offer a solution for these debilitating conditions. People who have suffered from a stroke have limited options for recovery the devastating effects of a stroke leave patients struggling with disabilities physically related to smell, taste, or frequent memory gaps, and different chronic health issues. The risk of developing strokes increases as you grow older but currently, 10-15% of stroke cases are observed in young people. Then, the procedure can be repeated or combined with other methods to increase therapy effectiveness.With an average of at least one person worldwide suffering from a stroke every 45 seconds, it is clear that treatment options are needed. The results are usually observed after several months. Then the patient goes home, and the stem cells begin their work. The transplant procedure lasts only forty minutes. They penetrate the brain and replace the damaged neurons exactly where the hematoma was formed. The resulting stem cells are injected into the patient intravenously. After that, the doctor selects stem cells and places them into a unique medium for cultivation. Therefore, the first stage isolates some active human cells and grows them to the necessary amount. For treatment, at least two hundred million stem cells will be required. As a result, stem cell therapy will allow you to recover after a stroke, prevent relapses, and remove all the illness causes: hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.įor treatment, cells are taken from the patient's tissues, particularly fatty tissue. They activate growing new neurons and blood vessels instead of those destroyed.

The treatment process is based on the unique abilities of stem cells to transform into different types of cells. Only cell therapy makes it possible to completely regenerate damaged brain tissue and return a patient to everyday life. One of the critical stages of stroke treatment is the restoration of the affected vessels and neurons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
